A car misfire occurs when one or more engine cylinders fail to ignite the fuel-air mixture properly. This leads to incomplete combustion. Common causes include defective spark plugs, fuel injector issues, or intake manifold gasket leaks.
Low fuel pressure and mechanical problems like low compression can also trigger misfires. Symptoms include rough acceleration, rough idle, vibrations, and a check engine light. Identifying the cause is crucial for fixing the issue promptly and ensuring smooth engine performance.
Can Cause a Car Misfire
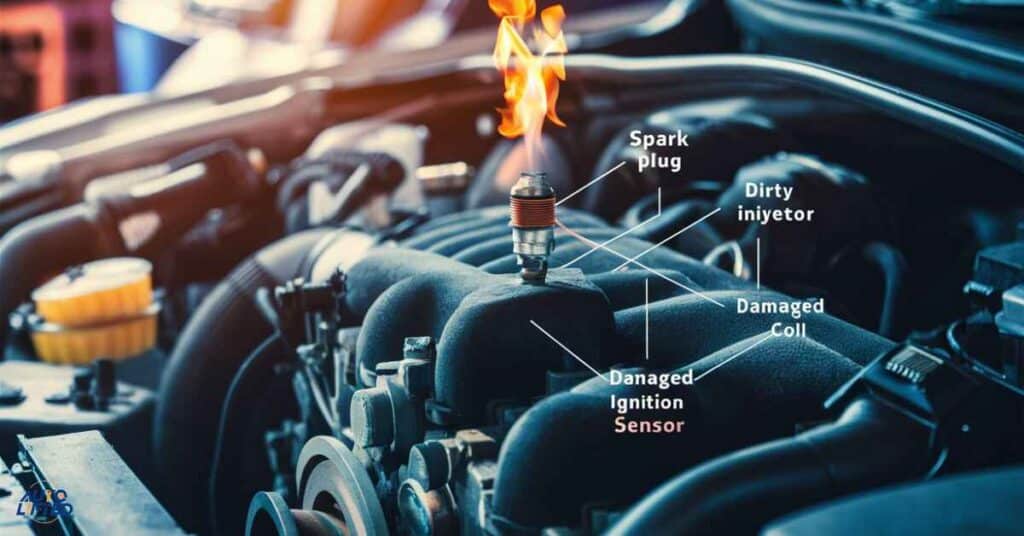
A car can misfire due to various issues such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coil problems, clogged fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or engine mechanical issues. Ignition system failures, like worn-out spark plugs or damaged ignition coils, can prevent proper combustion.
Fuel delivery problems, such as a clogged injector or weak fuel pump, lead to incorrect fuel-air mixtures. Vacuum leaks can disrupt the engine’s air intake, while sensor malfunctions can cause improper fuel metering.
Mechanical problems, including timing belt issues or low compression, also contribute to misfires. Identifying the root cause requires a comprehensive inspection of these systems.
Read This Blog:
How Many Axles Does A Car Have?
What Is a Misfire?

A misfire happens when the fuel in one or more of your engine’s cylinders fails to ignite properly. This can result from several issues, such as problems with the spark plugs, fuel injectors, or mechanical failures within the engine. Symptoms of a misfire include rough acceleration, rough idle, vibrations, and the check engine light turning on.
Finding the Cause
Identifying the exact cause of a misfire can be challenging due to the numerous potential culprits. Here are some steps to help pinpoint the issue:
Check Engine Light: Use an OBD-II scanner to read any error codes.
Inspect Spark Plugs: Look for signs of wear or damage.
Examine Fuel Injectors: Ensure they are not clogged or malfunctioning.
Test Fuel Pressure: Verify that the fuel pump and pressure regulator are functioning correctly.
Check Compression: Use a compression tester to ensure the engine’s cylinders are within the proper range.
The Most Common Reasons Why an Engine Will Misfire

Misfires can be caused by a variety of issues. Here are the most common reasons.
Defective Spark Plug
A defective spark plug can cause a car to misfire. Spark plugs are crucial for igniting the fuel-air mixture in the engine. When a spark plug is faulty or worn out, it can lead to incomplete combustion in the cylinder, resulting in engine misfires, rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency.
potentially even engine damage over time. Regular inspection and replacement of spark plugs are essential for maintaining optimal engine performance.
Intake Manifold Gasket Leaks
Intake manifold gasket leaks can cause a car to misfire. These gaskets seal the connection between the intake manifold and the engine block, ensuring proper airflow into the cylinders.
When the gasket deteriorates or develops a leak, unmetered air can enter the engine, disrupting the air-fuel mixture and leading to misfires. Symptoms may include rough idling, decreased engine performance, and potentially even engine stalling.
Prompt repair of intake manifold gasket leaks is crucial to prevent further engine damage and restore optimal performance.
Low Fuel Pressure
Low fuel pressure can cause a car to misfire. The fuel system relies on adequate pressure to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine cylinders for combustion. When fuel pressure is too low, the engine may receive insufficient fuel, leading to incomplete combustion and misfires.
Common symptoms include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and engine stalling. Causes of low fuel pressure can include a failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filter, or issues with the fuel pressure regulator.
Proper diagnosis and repair of low fuel pressure issues are essential to ensure smooth engine operation and prevent further damage.
Injector Issues
Injector issues can cause a car to misfire. Fuel injectors deliver precise amounts of fuel into the engine cylinders for combustion. When injectors become clogged, dirty, or malfunctioning, they may not spray fuel properly, leading to uneven combustion and misfires.
Symptoms of injector issues include rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and engine hesitation. Causes can include contaminated fuel, carbon buildup, or electrical problems affecting injector operation.
Regular maintenance, such as fuel system cleaning and using high-quality fuel, can help prevent injector issues. If misfires occur, diagnosing and addressing injector problems promptly is essential to restore engine performance and prevent further damage.
Low Compression or Damage Inside the Engine
Low compression or internal engine damage can lead to misfires. Compression is vital for creating the necessary pressure to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders.
When compression is low due to worn piston rings, damaged valves, or cylinder head gasket leaks, the engine may struggle to produce enough power, resulting in misfires. Symptoms include rough idling, lack of power, and engine vibrations.
Internal engine damage can also cause misfires, such as warped cylinder heads or scored cylinder walls. Proper diagnosis through a compression test or engine inspection is crucial to identify and address these issues.
Repairing low compression or internal damage may involve engine rebuilds or component replacements to restore optimal engine performance and prevent further misfires.
Wrong Air-Fuel Mixture
A wrong air-fuel mixture can cause a car to misfire. The engine requires a precise ratio of air to fuel for proper combustion. If this ratio is disrupted, either by too much air (running lean) or too much fuel (running rich), misfires can occur.
Lean mixtures can result from issues like vacuum leaks or a faulty mass airflow sensor, while rich mixtures may stem from a faulty fuel pressure regulator or dirty injectors. Symptoms include rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and engine hesitation.
Diagnosing and correcting the air-fuel mixture imbalance is essential to restore engine performance and prevent further damage. This may involve repairing or replacing components in the fuel or air intake system, as well as tuning engine parameters for optimal operation.
Also Read This Blog:
How Much Tip For Car Wash?
Symptoms of an Engine Misfire
Symptoms of an engine misfire include rough idling, vibrations, decreased engine power or acceleration, and an illuminated check engine light. Additionally, you may notice hesitation or jerking during acceleration, poor fuel efficiency, or a noticeable decrease in overall engine performance.
Misfires can also cause the vehicle to emit excessive exhaust emissions or produce unusual sounds from the engine. If left unresolved, misfires can lead to further damage to engine components, so it’s essential to address any symptoms promptly through diagnosis and repair.
Rough Acceleration
Rough acceleration is a common symptom of an engine misfire. During acceleration, the engine demands more power, and if one or more cylinders fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly, it can result in uneven power delivery and a sensation of hesitation or jerking.
This roughness may be particularly noticeable under load, such as when climbing hills or overtaking. Causes of rough acceleration include issues with spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or engine compression.
Diagnosing and addressing the underlying cause of the misfire is crucial to restore smooth acceleration and prevent further damage to the engine.
Rough Idle
Rough idle is a classic symptom of an engine misfire. When one or more cylinders fail to ignite fuel properly at idle, it can cause the engine to run unevenly, resulting in a shaky or vibrating sensation.
Causes of rough idle include issues with spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or engine compression problems. Additionally, a dirty throttle body or idle air control valve can contribute to rough idling.
Addressing the underlying cause of the misfire is essential to restore smooth engine operation at idle, improve fuel efficiency, and prevent further damage to engine components.
If you experience rough idle, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic to diagnose and resolve the issue promptly.
Check Engine Light
The illumination of the check engine light is often a sign of an engine misfire. Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostic systems that monitor various engine parameters, including cylinder performance.
When the engine control module detects a misfire, it triggers the check engine light to alert the driver to a potential issue. While a misfire is one of many potential causes for the check engine light to come on, it’s a significant one and should not be ignored.
Ignoring a misfire can lead to further damage to engine components and potentially higher repair costs. Therefore, if the check engine light comes on, it’s crucial to have the vehicle diagnosed by a qualified mechanic to identify and address the underlying problem promptly.
Slow Acceleration
Slow acceleration can be symptomatic of an engine misfire. When one or more cylinders fail to ignite fuel properly, it leads to reduced power output, resulting in sluggish acceleration. Misfires can be caused by issues such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or engine compression problems.
Additionally, air or vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, affecting engine performance. If you experience slow acceleration, it’s essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic to diagnose and address any underlying misfire issues promptly.
Ignoring misfires can lead to further damage to engine components and potentially compromise vehicle safety and performance.
A Change in the Engine’s Sound

A change in the engine’s sound can indicate an engine misfire. When one or more cylinders fail to ignite fuel properly, it disrupts the engine’s smooth operation, leading to irregular combustion and altering the engine’s typical sound.
You may notice unusual popping, sputtering, or roughness in the engine noise, particularly during acceleration or idle. These changes in sound can be caused by various factors, including faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or engine mechanical issues.
Ignoring changes in engine sound can lead to further damage and reduced performance. Therefore, it’s crucial to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic if you notice any unusual noises to diagnose and address any underlying issues, including potential misfires, promptly.
Other Common Causes
While the above reasons are the most typical causes of a misfire, other issues can also lead to this problem. These can include:
Vacuum Leaks: These can disrupt the air-fuel mixture.
EGR Valve Issues: A malfunctioning EGR valve can lead to incorrect exhaust gas recirculation, causing misfires.
Catalytic Converter Problems: A clogged catalytic converter can cause backpressure, leading to misfires.
How a Misfire Works
Understanding the mechanics of a misfire can provide insight into diagnosing and fixing the problem. When a cylinder misfires, it means that the combustion process within that cylinder did not complete properly.
This can be due to a lack of spark, improper fuel delivery, or insufficient compression. Addressing the root cause requires a thorough diagnostic process to pinpoint the specific issue and implement the appropriate repair.
Frequently Asked Question
How do you fix an engine misfire?
To fix an engine misfire, identify the faulty component like spark plugs or fuel injectors and replace or repair it. Regular maintenance checks can prevent future misfires.
How do I find out what is causing my misfire?
Use an OBD-II scanner to read error codes from the check engine light. Inspect spark plugs, fuel injectors, and perform compression tests for further diagnosis.
Will driving with a misfire damage my engine?
Yes, driving with a misfire can cause severe engine damage over time. It can lead to unburned fuel damaging the catalytic converter and other engine components.
Why is my car misfiring when I accelerate?
A car misfiring during acceleration can be due to faulty spark plugs, clogged fuel injectors, or insufficient fuel pressure. It may also indicate a vacuum leak or sensor issue.
Can a misfire correct itself?
A misfire rarely corrects itself and typically requires diagnosing and fixing the underlying issue. Ignoring it can lead to more serious engine problems.
Can low oil cause misfire?
Low oil levels generally do not cause misfires directly but can lead to engine damage. Lack of lubrication may cause components to wear out, potentially leading to misfires.
Final Thoughts
A car can misfire due to several reasons, primarily related to issues within the engine, fuel system, ignition system, or mechanical faults. Common causes include worn-out spark plugs or faulty ignition coils, which disrupt the spark needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
Fuel system problems, such as clogged injectors or a failing fuel pump, can lead to an improper fuel supply, causing the engine to run lean or rich. Additionally, vacuum leaks or issues with the engine’s sensors, like the oxygen sensor or mass airflow sensor, can result in incorrect air-fuel ratios.
Mechanical problems, such as a worn timing belt, low compression, or valve issues, can also contribute to misfires by disrupting the precise timing and operation of the engine’s components.
Diagnosing a misfire requires thorough inspection and often a combination of checking ignition, fuel delivery, and mechanical integrity to pinpoint and resolve the underlying issue.
