Chevrolet Malibu Won’t Start Top 14 Causes & Solutions is a comprehensive guide outlining common issues preventing a Malibu from starting and offering practical solutions to resolve them. It covers a range of potential culprits from fuel system issues to electrical problems empowering owners to troubleshoot and fix starting problems efficiently.
It trouble getting your Chevrolet Malibu to start. You are not alone. From fuel system issues to electrical gremlins there are numerous potential causes behind your car’s reluctance to start. In this comprehensive guide we will delve into the top 14 reasons why your Malibu might be having starting problems and provide practical solutions to help you troubleshoot and resolve the issue efficiently. It is a faulty battery a problem with the ignition system or a fuel related issue understanding these common culprits can empower you to get your Malibu back on the road in no time.
Common Causes of a Malibu Not Starting
Fuel System Problems: Issues like a faulty fuel pump clogged fuel filter or empty fuel tank can prevent the Malibu from starting.
Electrical System Failures: Problems with the battery alternator or starter motor may cause starting difficulties.
Ignition System Malfunctions: Faulty ignition switches spark plugs or ignition coils can hinder the starting process.
Mechanical Issues: Worn-out components like the timing belt crankshaft position sensor or fuel injectors may lead to starting problems.
Transmission Troubles: Transmission-related issues such as a faulty transmission control module or low transmission fluid levels can affect starting.
Engine Defects: Engine-related issues like a defective fuel injector oxygen sensor or catalytic converter can contribute to starting difficulties.
Hybrid System Glitches: Hybrid models may face starting issues due to faults in the hybrid battery pack or charging system.
Weather Sensitivity: Extreme temperatures or moisture can exacerbate existing problems making the Malibu more prone to starting issues.
Fuel-Related Issues

Fuel Pump Failure: A malfunctioning fuel pump can prevent proper fuel delivery to the engine leading to starting problems.
Clogged Fuel Filter: A blocked fuel filter restricts fuel flow hindering the engine’s ability to start.
Empty Fuel Tank: Running out of fuel or having an empty tank is a common cause of starting issues.
Fuel Injector Problems: Faulty fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel air mixture making it difficult for the engine to start.
Fuel Line Blockages: Blocked or clogged fuel lines can impede fuel flow to the engine resulting in starting difficulties.
Fuel Quality Issues: Contaminated or poor-quality fuel can affect engine performance and cause starting problems.
Fuel Pressure Regulator Failure: A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can lead to inconsistent fuel pressure affecting engine starting.
Vapor Lock: High temperatures can cause fuel to vaporize in the fuel lines disrupting fuel flow and preventing the engine from starting.
Fuel-related issues can significantly impact the starting of your Chevrolet Malibu. A malfunctioning fuel pump can disrupt proper fuel delivery to the engine leading to starting problems.
Electrical Issues

Battery Problems: A weak or dead battery can prevent the electrical system from providing enough power to start the engine.
Faulty Starter Motor: A malfunctioning starter motor may struggle to turn over the engine resulting in difficulty starting the vehicle.
Ignition Switch Failure: A faulty ignition switch can disrupt the electrical circuit needed to start the engine, leading to starting issues.
Bad Alternator: An alternator that fails to charge the battery properly can result in insufficient power for starting the engine.
Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the flow of electricity causing starting problems.
Ignition System Malfunction: Problems with components like spark plugs ignition coils or ignition modules can hinder the ignition process leading to starting difficulties.
Starter Solenoid Problems: Issues with the starter solenoid such as worn contacts or electrical faults can prevent the starter motor from engaging properly.
Faulty Fuses or Relays: Blown fuses or faulty relays in the electrical system can interrupt power flow to crucial components affecting starting performance.
Also read this:
Ford Explorer Won’t Start? Here’s Quick Solutions To The Most Common Causes
Mechanical Issues
Timing Belt Failure: A broken or worn timing belt can cause the engine’s timing to become misaligned resulting in starting issues.
Fuel System Problems: Issues such as a clogged fuel filter fuel pump failure or fuel injector issues can disrupt the proper delivery of fuel to the engine affecting starting.
Engine Compression Loss: Loss of compression in the engine cylinders due to worn piston rings cylinder head gasket leaks or valve problems can lead to starting difficulties.
Faulty Crankshaft or Camshaft Position Sensor: Malfunctioning sensors can cause incorrect timing signals to be sent to the engine control unit resulting in starting problems.
Exhaust System Blockages: Blockages in the exhaust system such as a clogged catalytic converter or muffler can restrict airflow and affect engine starting.
Overheating: Engine overheating due to cooling system failures or low coolant levels can lead to starting issues as the engine may struggle to turn over.
Air Intake Issues: Problems with the air intake system such as a dirty air filter or intake manifold leaks can disrupt the air fuel mixture ratio needed for starting.
Valve Train Problems: Issues with components like bent valves worn valve springs or stuck valves can affect engine compression and starting performance.
Troubleshooting Steps
Check the Fuel System
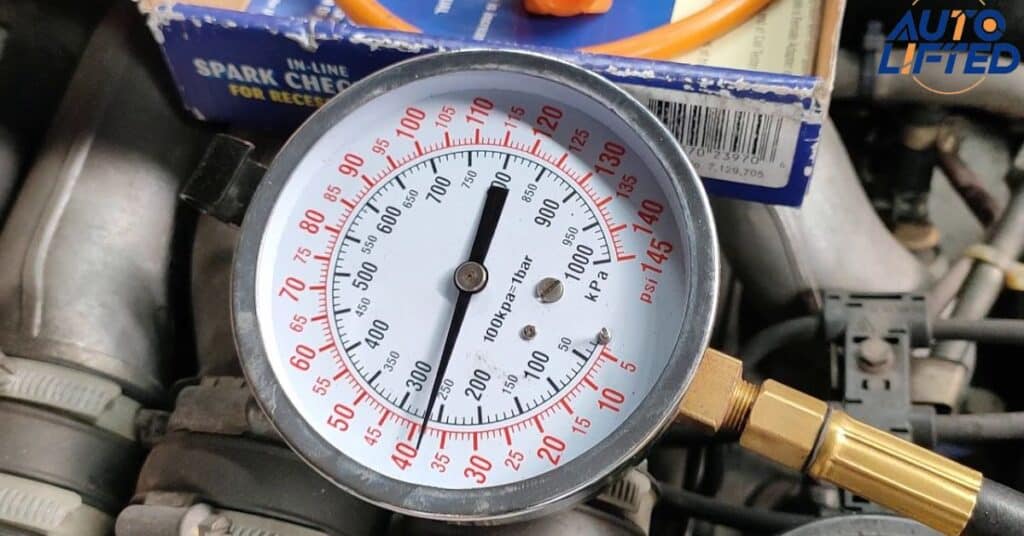

Checking the fuel system is crucial when diagnosing starting issues with your Chevrolet Malibu. Here are steps to take.
Verify Fuel Level: Always start by ensuring there’s enough fuel in the tank for the engine to start.
Inspect Fuel Pump Operation: Listen for the characteristic humming sound of the fuel pump when you turn the ignition key to the ON position. If you don’t hear it there might be an issue with the fuel pump.
Examine Fuel Lines: Visually inspect the fuel lines for any signs of leaks corrosion or damage. Even small leaks can prevent the engine from getting enough fuel.
Test Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to check if the fuel pressure meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Low fuel pressure can indicate a problem with the fuel pump or fuel pressure regulator.
Check Fuel Filter: Ensure the fuel filter is not clogged or dirty as this can restrict fuel flow to the engine. If the filter is dirty, it should be replaced.
Inspect Fuel Injectors: Make sure the fuel injectors are clean and functioning properly. Clogged or faulty fuel injectors can prevent the engine from getting the right amount of fuel
Review Fuel Quality: Ensure you are using the correct octane-rated fuel for your Malibu. Contaminated or low-quality fuel can cause starting issues.
Address Fuel Pump Relay: Test the fuel pump relay and replace it if it is faulty. The relay controls power to the fuel pump so if it is not working correctly the fuel pump may not receive power leading to starting problems.
Check the Electrical System
Checking the electrical system is vital for diagnosing starting issues in your Chevrolet Malibu. Here’s how to proceed
Inspect Battery: Begin by checking the battery terminals for corrosion and ensuring they are securely connected. A weak or dead battery can prevent the engine from starting.
Test Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage across the battery terminals. A fully charged battery should have around 12.6 volts. Anything significantly lower may indicate a faulty battery.
Check Alternator: Verify that the alternator is charging the battery properly. You can do this by testing the alternator output voltage with the engine running. It should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
Examine Starter Motor: Inspect the starter motor for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure the electrical connections to the starter are tight and secure.
Test Ignition Switch: Check the ignition switch for proper operation. A faulty ignition switch can prevent power from reaching the starter motor, causing starting issues.
Inspect Spark Plugs: Ensure the spark plugs are in good condition and properly gapped. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause ignition problems leading to difficulty starting the engine.
Review Ignition Coils: Test the ignition coils to ensure they are sending strong, consistent spark to the spark plugs. Faulty ignition coils can result in weak or inconsistent spark affecting engine starting.
Check Fuses and Relays: Inspect the fuses and relays related to the starting and ignition system. A blown fuse or faulty relay can interrupt power flow and prevent the engine from starting.
Check the Mechanical System

Check the Mechanical System
Inspect Timing Belt: Examine the timing belt for any signs of wear damage or misalignment. A broken or improperly timed timing belt can prevent the engine from starting.
Test Crankshaft Position Sensor: Verify that the crankshaft position sensor is functioning correctly. A faulty sensor can disrupt the engine’s timing and ignition leading to starting issues.
Examine Ignition System Components: Inspect ignition system components such as the distributor rotor and ignition coil for wear or damage. Faulty ignition components can result in weak or inconsistent spark affecting engine starting.
Check Engine Compression: Perform a compression test to check the compression levels in each cylinder. Low compression can indicate issues such as worn piston rings or damaged valves affecting engine starting.
Inspect Fuel System Components: Ensure components of the fuel system including the fuel rail injectors and pressure regulators are in good condition and functioning properly. Any faults in the fuel system can hinder engine starting.
Review Air Intake System: Check the air filter and intake ducts for any obstructions or damage. A restricted air intake can affect the air-fuel mixture and hinder engine starting.
Test Engine Sensors: Test various engine sensors such as the throttle position sensor (TPS) and mass airflow sensor (MAF) to ensure they are sending accurate signals to the engine control unit (ECU). Malfunctioning sensors can disrupt engine operation and starting.
Inspect Exhaust System: Examine the exhaust system for leaks cracks or damage. A faulty exhaust system can affect engine performance and starting by disrupting proper engine breathing and exhaust flow.
| Related Topics |
| Engine Compression Test |
| Timing Belt Inspection |
| Crankshaft Sensor Testing |
| Camshaft Sensor Testing |
| Ignition System Check |
| Fuel Injection Inspection |
| Air Intake Examination |
| Exhaust System Inspection |
| Engine Sensor Assessment |
Specific Issues by Year/Model/Engine
First Generation (1964-1967)
First Generation Overview: The Chevrolet Malibu’s debut generation from 1964 to 1967 epitomized the essence of mid-century American automotive excellence. With its iconic design and robust performance, it quickly captured the hearts of drivers seeking both style and power.
Classic Design: Embodying the spirit of the ’60s the first-generation Malibu featured sleek lines chrome accents and a distinctively bold presence on the road. Its timeless aesthetic continues to resonate with collectors and enthusiasts alike.
Powerful Engines: Under the hood a range of potent V8 engines offered exhilarating performance delivering a thrilling driving experience synonymous with American muscle cars of the era.
Comfort and Luxury: Inside the cabin the Malibu provided a spacious and comfortable environment with premium materials and thoughtful amenities ensuring an enjoyable ride for drivers and passengers alike.
Enduring Legacy: The first generation Malibu left an indelible mark on automotive history serving as a testament to Chevrolet’s commitment to craftsmanship innovation and driving pleasure.
Collectible Status: Today well preserved examples of the first generation Malibu are highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts reflecting its enduring appeal and cultural significance.
Iconic Status: From its distinctive styling to its powerful performance the first generation Chevrolet Malibu remains a cherished symbol of American automotive ingenuity and craftsmanship.
Second Generation (1978-1983)
Second Generation Overview: The Chevrolet Malibu’s second generation spanning from 1978 to 1983 marked a transition towards a more modern and fuel efficient era. It retained its classic American design while embracing technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences.
Efficient Design: With a focus on fuel efficiency and aerodynamics the second generation Malibu featured a more streamlined exterior design reflecting the changing automotive landscape of the late 70s and early 80s.
Advanced Features: This generation introduced new features and technologies aimed at enhancing driver comfort and convenience such as power windows air conditioning, and improved sound insulation making the Malibu a more refined and enjoyable ride.
Variety of Powertrains: From economical inline-four engines to powerful V8 options the second-generation Malibu offered a diverse range of powertrain choices to cater to different driving preferences and needs.
Increased Safety: Safety considerations became more prominent during this era leading to the integration of advanced safety features such as improved braking systems reinforced chassis and optional airbags enhancing occupant protection.
Cultural Impact: The second generation Malibu reflected the shifting automotive trends of its time embracing a balance between performance efficiency and comfort making it a popular choice among families and commuters alike.
Heritage and Legacy: Despite facing competition from imports and changing market dynamics the second generation Malibu continued to uphold Chevrolet’s legacy of quality reliability and innovation leaving an enduring mark on American automotive history.
Third Generation (1997-2003

1997-1999 Model Years: These early models of the third generation equipped with the 2.4 liter engine may experience issues like rough idling or stalling due to a faulty crankshaft position sensor.
2000-2003 Model Years (3.1-liter Engine): Malibu’s with the 3.1 liter engine during this period might suffer from coolant leaks originating from the intake manifold gasket potentially leading to engine overheating.
Throttle Position Sensor Problems: Some 2000-2003 models with the 3.1 liter engine may also encounter hesitation or stalling during acceleration due to a faulty throttle position sensor.
Ignition Switch Issues (2002-2003): Certain 2002-2003 models might face problems with the ignition switch which can cause the engine to stall or shut off while driving prompting a recall for affected vehicles.
Transmission Troubles: Transmission issues including hard shifting slipping gears or complete failure have been reported in some third generation Malibu’s necessitating professional diagnosis and repair.
Maintenance Vitality: Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs are crucial for addressing these issues and ensuring the longevity and reliability of third generation Malibu models.
Fourth Generation (2004-2007)
2004 Model Year: Some Malibu’s of this year may experience premature power steering pump failure leading to difficulty steering or loss of power steering.
ABS System Problems: Owners of 2004 Malibu’s might encounter issues with the anti-lock brake system (ABS) light illuminating due to faults in wheel speed sensors or control modules.
Fuel Injector Issues (2004): Malibu’s with the 2.2L engine in 2004 may suffer from fuel injector problems causing rough idling power reduction and poor fuel economy.
Timing Chain Tensioner (2005): Certain 2005 Malibu’s with the 3.5L V6 engine may experience timing chain tensioner failure resulting in engine rattling and potential damage.
Fuel Tank Venting (2005): Some 2005 Malibu’s could have issues with the fuel tank not venting correctly leading to difficulties in refueling and potential stalling while driving.
Ignition Switch Failure (2006): Owners of 2006 Malibu’s may encounter problems with the ignition switch failing, causing intermittent starting issues or stalling while driving.
Fifth Generation (2008-2012)
2008 Model Year: Some owners faced power steering system issues causing a loss of power assist alongside transmission problems like erratic shifting.
2009 Model Year: Electrical stability control system troubles led to unexpected engagement while driving alongside transmission and power door lock issues.
2010 Model Year: Common problems included fuel pump relay issues causing stalling power steering system concerns and engine performance issues.
2011 Model Year: Air conditioning system troubles emerged alongside transmission and electrical system issues reported by owners.
2012 Model Year: Issues included excessive oil consumption electrical system problems and transmission issues requiring attention for proper functioning.
Sixth Generation (2013-2015)
2013 Model Year: Reported problems included transmission shifting issues electrical problems and excessive oil consumption.
2014 Model Year: Owners experienced electrical issues air conditioning problems and inaccurate fuel gauge readings.
2015 Model Year: Engine problems infotainment system issues and suspension problems were reported by some owners.
Seventh Generation (2016-Present)

2016-2018 Models: Power steering and transmission issues were common along with infotainment system malfunctions.
2016-2019 Models: Reported transmission problems included rough shifting and hesitation while hybrid models had issues with the hybrid system.
2016-2020 Models: Owners reported problems with the infotainment system including radio and Bluetooth connectivity issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I reset my Chevy key?
To reset your Chevy key you can try reprogramming it using the vehicle’s onboard programming feature or consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions tailored to your model.
How do I program my Chevy Malibu key?
To program your Chevy Malibu key follow the step-by step instructions outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult a professional locksmith for assistance.
How do you fix an unresponsive key fob?
To fix an unresponsive key fob try replacing the battery reprogramming the key or consulting a dealership or locksmith for further assistance.
Why do Chevy Malibu have 2 batteries?
Chevy Malibu Hybrid models may have two batteries to power both the traditional combustion engine and the electric motor contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Does the Chevy Malibu have 2 batteries?
The standard Chevy Malibu typically has one battery while the hybrid models may incorporate a secondary battery to support the electric components.
Why is my remote start not working and check engine light on?
The remote start might not work due to a malfunctioning component linked to the check engine light indicating a problem that needs diagnosis and repair to restore functionality.
Can I start my Chevy Malibu with my phone?
Certain models of the Chevy Malibu offer remote start functionality through smartphone apps like my Chevrolet enabling users to start their vehicles remotely.
How do you start a Chevy Malibu after theft system?
To start a Chevy Malibu after the theft system is activated perform a reset by turning the key to the on position for 10-15 minutes until the theft system light stops flashing. Then, turn it off and try starting the car again.
Which Malibu has remote start?
The Chevy Malibu LT and Premier trims typically come equipped with remote start functionality.
How does Chevy start stop work?
Chevy’s start-stop system automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle comes to a stop such as at a traffic light and restarts it when the driver lifts off the brake pedal saving fuel and reducing emissions.
How do you start a keyless car?
To start a keyless car simply press the brake pedal and then push the engine start button often located on the dashboard or center console.
Can I start my Chevy with my phone?
You can start some Chevy models with your phone using my Chevrolet app’s remote start feature.
Conclusion
when faced with a Chevrolet Malibu that won’t start it is essential to consider various factors to pinpoint the root cause. By checking the fuel system electrical components and mechanical parts one can troubleshoot effectively. The following proper maintenance routines and addressing issues promptly can prevent future starting problems.
Remember a dead battery faulty ignition switch or fuel system malfunction could be behind the issue. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can ensure a smooth driving experience and minimize the inconvenience of a non-starting Malibu. Trusting professional mechanics and staying vigilant can keep your Malibu on the road reliably.

Passionate automotive enthusiast sharing insights, tips, and stories from the world of cars. Join me on an exhilarating journey through the roads of automotive excellence.
